High-grade Tear Of Anterior Talofibular Ligament
DiagnosisYour diagnosis is a complete (Grade III) tear of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Injury or ConditionThis injury is a total disruption of the most important stabilizing ligament in the knee. The anterior cruciate ligament is located centrally within the knee, behind the kneecap, making it difficult for the to specifically localize the injury. CauseThe most common cause is a knee hyperextension with a twist (torsion) which occurs while the knee is momentarily unprotected by the surrounding musculature, especially your hamstrings. The injury typically occurs during sports such as skiing, basketball and soccer and may occur at surprisingly low force applications. SymptomsTypical symptoms are a “pop” at the time of the initial injury followed by swelling which appears within the first 24 hours. Pain may be minimal initially if the ACL alone is damaged.
Athletes who attempt to return to action may experience a second episode of instability (pivoting). TreatmentOur standard treatment should include:. Ice, elevation and compression to control swelling. Walking (weight-bearing) is preferable if muscular control of the injured leg is adequate. Knee straightening (extension) and bending (flexion) are encouraged by gentle stretching, stationary cycling and/or pool therapy. Arthroscopic surgery should be undertaken in young, active patients because the ACL will not heal unless surgically restored.
A single hamstring tendon from the back of your thigh is the preferred graft. In older or less active patients, exercise therapy like cycling with a toe-clip and bracing of the knee may be selected as optimal treatment, as long as instability is not present. This patient group should avoid aggressive sports in the future.
Anterior Talofibular Ligament Injury

If the shock-absorbing cartilages (menisci) are torn extensively, surgery may be required even in less active patients.PrecautionsImportant precautions:. Avoid excessive swelling in your knee, calf and ankle regions by conscientious elevation and frequent muscle contractions. In cases where surgical treatment is necessary, make sure that early knee stiffness is improving prior to surgery. 120 degrees of flexion is recommended prior to surgery. Avoid aspirin. Be sure you understand your injury and treatment thoroughly.
Complete rupture of the ACL can affect knee function for a lifetime and can lead to osteoarthritis if not treated correctly. Do not participate in jumping, cutting or twisting sports until you have recovered fully from you injury, and the doctor has cleared you to do so.Recovery. When arthroscopic reconstruction is necessary, walking in a protective brace is begins within 1-2 weeks of surgery. Optimal rehabilitation is staged for return to aggressive sports activities or heavy labor after approximately six months. Expected recovery for those who do not need surgical intervention usually occurs in three months at which time swelling should be resolved and strength is usually recovered.
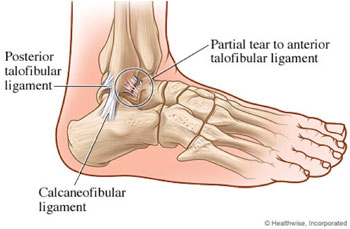
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.Ankle ligament tear treatment may include a combination of rest, exercise and rehabilitation. Surgery is sometimes needed for severe ankle sprains. TipsDepending on the severity of your ligament injury, initial treatment may include anti-inflammatory medication and physical therapy modalities such as ultrasound and electrical stimulation to decrease pain and swelling. As healing progresses, range-of-motion and strengthening exercises are added.Read more. Grading Ankle InjuriesAnkle sprains are categorized and treated based on the severity of the ligament injury. Grade 1 sprains involve ligament stretching without obvious tearing.
A grade 2 ankle sprain describes a partial ligament tear, and grade 3 sprains involve complete tearing of one or more ankle ligaments. Ankle Ligament Tear TreatmentInitial ankle ligament tear treatment during the acute phase of healing — the first few days after the injury — focuses on reducing pain and inflammation. Ice packs can be applied for up to 20 minutes every 3 to 4 hours, beginning immediately after injury. Cold application helps decrease pain by making your nerves less sensitive and is most effective for the first few days after injury, according to the.Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve) or aspirin, may alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during this phase. Elevating your leg as much as possible helps limit and reduce swelling. Your doctor may recommend crutches, a supportive boot, elastic bandage and/or a splint to protect your ankle from further injury. Interventions in the Subacute PhaseThe subacute phase of healing begins around day four and continues until 2 weeks after an ankle ligament injury.
During this phase, range-of-motion exercises begin to decrease ankle stiffness caused by swelling. You might receive physical therapy, including ultrasound and electrical stimulation, to help promote healing and exercises to improve your mobility.drawing the alphabet in the air with your toes, ankle circles, gentle stretches and possibly non-weight-bearing activities, such as riding a stationary bike. You might begin to put some weight on your foot as you walk, if approved by your doctor. Time to Get MovingThe rehabilitation phase of treatment typically begins once you are able to bear full weight on your ankle and no longer need crutches to walk. This phase may begin 2 to 6 weeks after injury, with more severe ligament tears at the later end of that time frame.The goal of this phase is to regain movement, strength and function in your ankle. Your physical therapist may stretch your ankle to decrease stiffness and improve movement., towel toe scrunches and toe marble pick-up, may be performed.Read more: Restore Full FunctionSix weeks after injury and beyond, treatment for ankle ligament tear treatment focuses on returning to full function.

Range-of-motion exercises continue with added resistance from an elastic band. Balance training activities, such as standing on an uneven surface and standing only on your injured leg, are also included in treatment.
Functional activities might also include sports and recreational activities, jumping and running. Surgery for Ankle SprainsSevere grade 3 sprains may require surgery, particularly if you have ongoing pain or consistently feel like your ankle is going to give out. In these situations, your torn ankle ligaments may be reattached with screws. You may have to wear a cast and use crutches for 6 to 8 weeks while the ligament heals.
Complete Tear Anterior Talofibular Ligament
Once the cast is removed, treatment begins at the subacute phase and progresses through the rehab and functional phases. Warnings and PrecautionsSeek medical attention if you sprain your ankle, even if you think it's just a minor injury. Early treatment can prevent long-term issues with loss of motion and chronic weakness that can develop after this injury.